Portfolio Management Explained: Definition, Importance & Examples
Managing money is no longer just about picking a few good investments and hoping for the best. In today’s uncertain and fast-moving markets, investors need structure, discipline, and clarity. This is where the importance of portfolio management becomes impossible to ignore. A well-managed portfolio helps investors control risk, align investments with goals, and stay focused during market ups and downs.
For beginners and experienced investors alike, portfolio management explained in simple terms helps remove confusion and emotional decision-making. When investors understand the portfolio management definition clearly, they are better equipped to make informed choices that support long-term financial stability.
Turn strategy into results with expert portfolio management support.
Portfolio Management Explained in Simple Terms
Portfolio management explained simply means planning, selecting, monitoring, and adjusting investments to meet financial goals. It is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process that evolves with markets and life stages.
The importance of portfolio management lies in creating balance. Instead of relying on a single asset, portfolio management spreads investments across different instruments to reduce risk and improve consistency.
What portfolio management means for investors
Selecting the right mix of assets
Aligning investments with goals
Managing risk exposure
Reviewing performance regularly
Making adjustments when required
Why portfolio management is relevant today
• Markets are highly volatile
• Investment choices are increasing
• Emotional investing can cause losses
• The importance of portfolio management grows during uncertainty
Portfolio Management Definition and Core Concept
The portfolio management definition refers to the systematic process of managing a collection of investments to achieve specific financial objectives while controlling risk.
Understanding the portfolio management definition helps investors see the bigger picture rather than focusing on individual returns.
Formal portfolio management definition
Portfolio management involves asset allocation, diversification, monitoring, and rebalancing of investments to optimize returns within acceptable risk limits.
Focuses on overall portfolio performance
Considers risk and return together
Aligns investments with objectives
Requires continuous evaluation
How portfolio management works in practice
Portfolio management explained in practice includes choosing assets, tracking performance, and making informed changes.
• Asset selection based on goals
• Periodic portfolio review
• Rebalancing to maintain allocation
• Risk management adjustments
Importance of Portfolio Management for Investors
The importance of portfolio management becomes clear when investors face market fluctuations, economic changes, or personal financial transitions.
Without structure, investors often react emotionally. Portfolio management provides discipline and direction.
Why portfolio management is essential
Reduces overall investment risk
Improves return consistency
Prevents overexposure to one asset
Encourages long-term thinking
Impact on long-term wealth creation
The importance of portfolio management lies in its ability to support compounding. Proper management allows investors to stay invested, rebalance gains, and protect capital during downturns.
Read More: What is PMS in Stock Market A Complete Guide in 2025
Objectives of Portfolio Management
Every portfolio is built with specific objectives in mind. Portfolio management explained clearly helps investors understand these objectives.
Key objectives of portfolio management
Capital appreciation
Income generation
Liquidity management
Capital protection
Risk control
Aligning objectives with investor goals
Portfolio management explained properly ensures that objectives match the investor’s time horizon, income needs, and risk tolerance.
Read More: Difference Between SIP and Mutual Fund Explained: A Complete Guide for New Investors
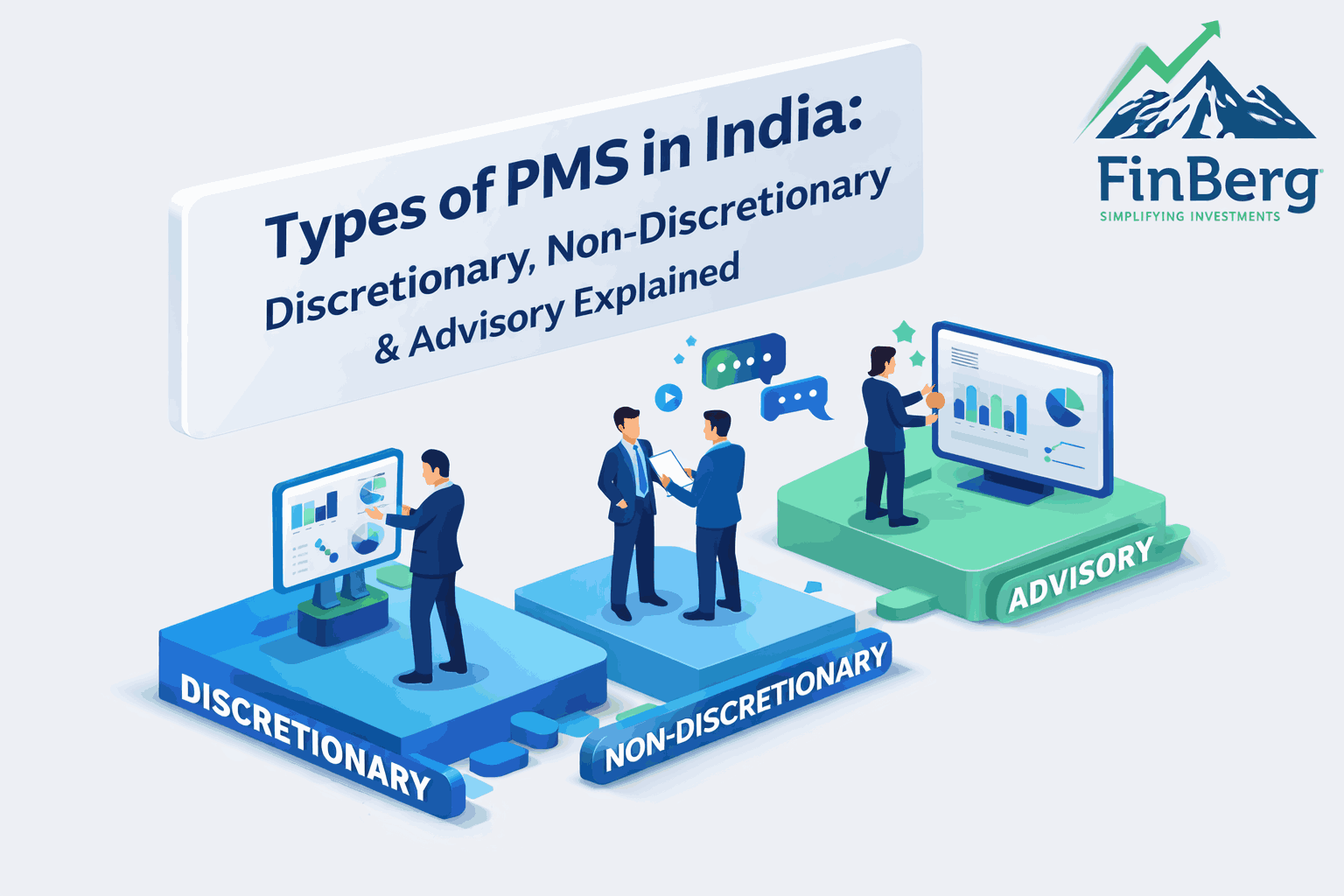
Types of Portfolio Management
There are different approaches to portfolio management, each serving different investor preferences.
Active portfolio management
Active portfolio management involves frequent monitoring and decision-making.
• Regular buying and selling
• Market research and analysis
• Higher involvement
• Aims to outperform benchmarks
Passive portfolio management
Passive portfolio management follows predefined strategies.
Index-based investing
Lower turnover
Reduced costs
Long-term discipline
Both approaches highlight the importance of portfolio management in maintaining structure.
Portfolio Management Explained Through Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is the foundation of portfolio management explained in practical terms.
It determines how investments are distributed across asset classes.
Role of asset allocation
• Balances risk and return
• Diversifies investments
• Aligns portfolio with goals
• Strengthens portfolio stability
Strategic vs tactical allocation
Strategic allocation focuses on long-term goals
Tactical allocation adjusts for short-term opportunities
Both support the importance of portfolio management
Combined approach improves flexibility
Read More: How to Buy and Sell Unlisted Shares in India: A Step-by-Step Investor’s Guide
Risk Management and Portfolio Management
Risk is unavoidable, but it can be managed effectively.
The importance of portfolio management lies in controlling risk rather than eliminating it.
How portfolio management helps control risk
• Diversification across assets
• Limiting concentration risk
• Managing volatility exposure
• Aligning risk with tolerance
Balancing risk and return
Portfolio management explained well shows that higher returns usually involve higher risk. Managing this balance is central to successful investing.
Examples of Portfolio Management
Real-world examples help explain portfolio management explained clearly.
Example 1: Conservative investor portfolio
Higher allocation to debt
Lower equity exposure
Focus on income stability
Low volatility
Example 2: Moderate investor portfolio
• Balanced equity and debt
• Moderate risk
• Stable growth
• Long-term orientation
Example 3: Aggressive growth portfolio
Higher equity allocation
Greater volatility
Long-term horizon
Focus on capital appreciation
Each example reinforces the importance of portfolio management.
Portfolio Management Explained for Different Life Stages
Investment needs change over time.
Portfolio management explained by life stage helps investors adapt strategies.
Early-career investors
• Higher risk capacity
• Long investment horizon
• Focus on growth
• Equity-heavy portfolios
Mid-career investors
Balance between growth and safety
Increasing responsibilities
Gradual risk reduction
Retired or near-retirement investors
• Income focus
• Capital preservation
• Lower volatility
• Stable allocation
Portfolio Monitoring and Rebalancing
Portfolio management does not end after investing.
The importance of portfolio management includes continuous monitoring.
Why regular portfolio reviews matter
Track performance
Identify allocation drift
Respond to market changes
Stay aligned with goals
Rebalancing strategies
• Periodic rebalancing
• Threshold-based rebalancing
• Market-driven adjustments
Read More: Comparing the Best PMS Companies in India: Performance, Fees, and Services Explained
Common Portfolio Management Mistakes
Many investors overlook the importance of portfolio management.
Mistakes investors make without proper management
• Overconcentration
• Emotional decisions
• Ignoring asset allocation
• Chasing short-term returns
How portfolio management helps avoid these errors
Portfolio management explained properly promotes discipline, planning, and rational decision-making.
Tools and Techniques Used in Portfolio Management
Modern investing uses tools to improve efficiency.
Tools used by investors and advisors
Risk profiling tools
Asset allocation models
Performance tracking systems
Analytics platforms
Role of professional guidance
Professionals apply the portfolio management definition systematically, ensuring alignment with objectives and market conditions.
Learn More: Equity Fund Investment vs. Mutual Fund: Which Is Better for 2025?
Portfolio Management Overview
Importance of Portfolio Management in Volatile Markets
Market volatility tests investor patience.
The importance of portfolio management increases during uncertain times.
Managing market uncertainty
• Reduces panic decisions
• Protects capital
• Maintains allocation discipline
Maintaining long-term focus
Portfolio management explained helps investors stay committed to long-term goals despite short-term fluctuations.
Read More: How to Choose the Best Pre-IPO Investment Platform: A Beginner’s Guide
How to Build an Effective Portfolio Management Strategy
Building a strategy requires clarity and structure.
Key factors to consider
Financial goals
Risk tolerance
Time horizon
Liquidity needs
Market conditions
Step-by-step portfolio management approach
Define objectives
Assess risk profile
Allocate assets
Monitor performance
Rebalance periodically
Contact us to get expert guidance for your investment goals
Conclusion
Portfolio management explained clearly shows that investing success depends on structure, discipline, and adaptability. Understanding the portfolio management definition allows investors to move beyond guesswork and emotional decisions.
The importance of portfolio management lies in its ability to manage risk, support long-term wealth creation, and keep investments aligned with goals. Whether an investor is conservative or aggressive, effective portfolio management remains the foundation of sustainable financial success.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is portfolio management explained in simple terms?
Portfolio management explained means managing investments systematically to achieve financial goals while controlling risk.
2. Why is the importance of portfolio management high for investors?
Because it reduces risk, improves consistency, and supports long-term financial planning.
3. What is the correct portfolio management definition?
It is the process of selecting, monitoring, and adjusting investments to optimize returns within acceptable risk levels.
4. How does portfolio management help reduce risk?
Through diversification, proper asset allocation, and regular rebalancing of investments.
5. Can beginners benefit from portfolio management explained clearly?
Yes, beginners gain structure, discipline, and clarity when portfolio management is explained properly.
6. How often should portfolios be reviewed?
Portfolios should be reviewed at least once a year or whenever major financial or market changes occur.
7. Is professional guidance necessary for portfolio management?
Professional guidance helps improve structure, discipline, and decision-making, especially for long-term goals.
8. What assets are included in portfolio management?
Equity, debt instruments, and alternative investments are commonly included.
9. How does portfolio management differ by age?
Younger investors focus more on growth, while older investors prioritize stability and income.
10. What happens without proper portfolio management?
Without proper portfolio management, investors face higher risk, emotional decisions, and inconsistent returns.
Powered by Froala Editor